ShyderChat
desenvolvido usando a api oficial do facebook
revolucionário, o primeiro e completo software de marketing do mundo para facebook e outras mídias sociais desenvolvido usando apis oficiais.
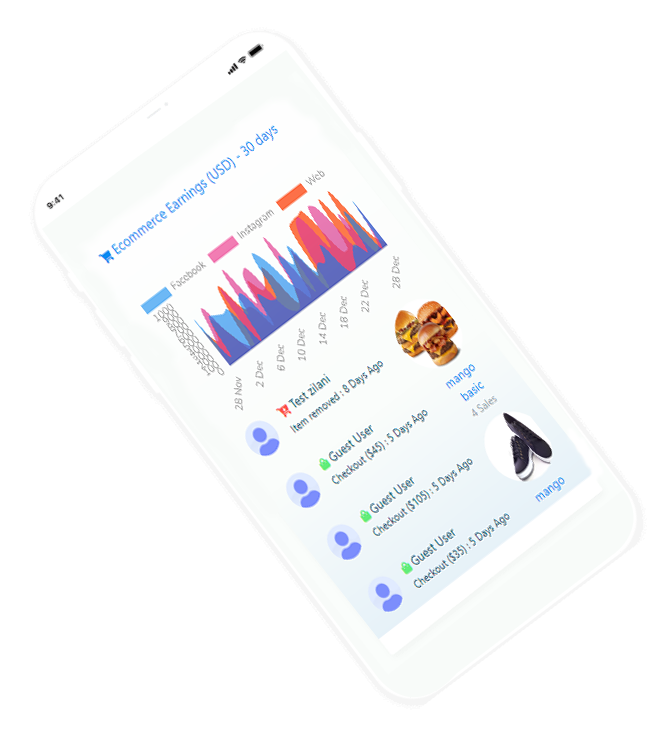
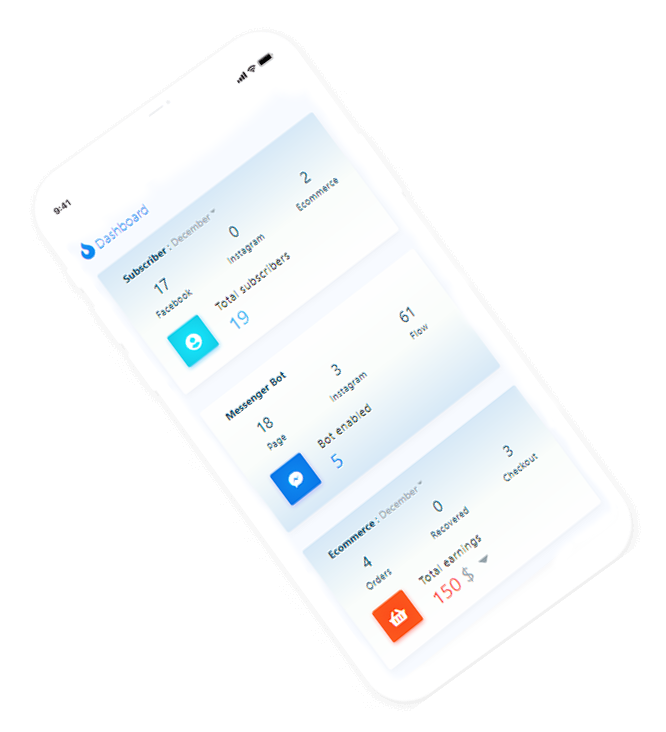


revolucionário, o primeiro e completo software de marketing do mundo para facebook e outras mídias sociais desenvolvido usando apis oficiais.




configure o bot do messenger para responder 24 horas por dia, 7 dias por semana, com o construtor de fluxo visual.
chat ao vivo com assinantes do facebook/instagram
template, ocultar/excluir comentário ofensivo, resposta baseada em palavras-chave, resposta genérica a comentários de postagens de páginas do Facebook.
postagem instantânea/agendada nas mídias sociais.

alguns passos para conectar sua conta do facebook e instagram e fazer este aplicativo funcionar.


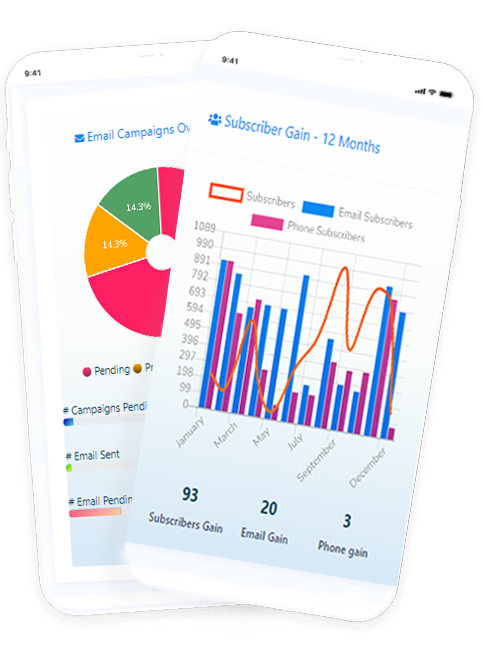
aqui estão algumas capturas de tela de como fica. veja as fotos incríveis e divirta-se.
nós fornecemos a você um pacote de teste, para que você possa ver a grandiosidade em ação e explorá-la mais.
